Understanding Cataracts: Causes, Symptoms, Types, and Prevention
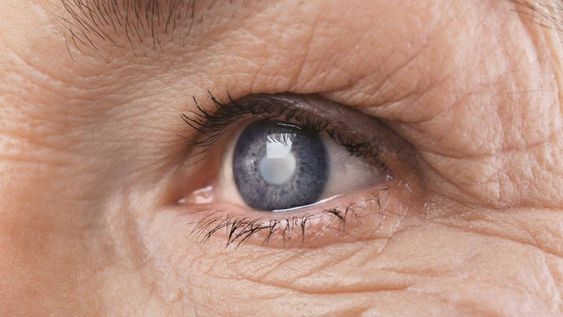
Cataracts are a prevalent eye condition that primarily affects older adults. They occur when the lens of the eye, which is normally clear, becomes cloudy due to the gradual breakdown of proteins. This clouding can significantly impair vision, making everyday activities like reading, driving, or even watching television more challenging.
What Causes Cataracts?
The primary cause of cataracts is aging, as the natural proteins in the lens of the eye deteriorate over time. However, other factors can also contribute to their development, including:
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of cataracts can increase your likelihood of developing them.
- Environmental Influences: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a significant risk factor. Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor nutrition may also contribute.
- Medical Conditions: Certain health issues, such as diabetes, can increase the risk of cataract formation. Long-term use of corticosteroid medications can also accelerate the process.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Cataracts typically develop slowly, and many people may not notice symptoms in the early stages. However, as they progress, you may experience:
- Cloudy or Blurred Vision: Your sight may become increasingly unclear, akin to looking through a foggy window.
- Difficulty Seeing at Night: You may find it harder to see in dim lighting, impacting activities like driving after dark.
- Sensitivity to Light and Glare: Bright lights can be uncomfortable, and you may have trouble with glare from the sun or headlights.
- Halos Around Lights: You might see a halo effect around streetlights or car headlights, especially at night.
- Frequent Changes in Eyeglass Prescription: If you find that your glasses need constant adjustment, it could be a sign of cataracts.
- Fading or Yellowing of Colors: Colors may appear less vibrant or take on a yellow tint.
- Double Vision in One Eye: This can occur as a result of the cataract affecting the lens.
Types of Cataracts
There are several types of cataracts, each with distinct characteristics:
Nuclear Cataracts: These are the most common type, typically developing in the center of the lens as people age. They tend to progress slowly and are associated with gradual cloudiness of vision.
Cortical Cataracts: These cataracts form around the outer edge of the lens. They can create visual distortions, particularly in bright light or glare, and can affect peripheral vision.
Subcapsular Cataracts: Located at the back of the lens, these cataracts may develop more rapidly and are often linked to conditions like diabetes or prolonged use of steroid medications.
Congenital Cataracts: These cataracts can be present at birth or develop during early childhood, often due to genetic factors or maternal infections during pregnancy.
Can Cataracts Be Prevented?
While cataracts cannot be entirely prevented, there are effective strategies to slow their progression:
UV Protection: Protecting your eyes from harmful UV rays is essential. Wearing sunglasses that provide 100% UV protection when outdoors can significantly reduce risk. If you wear eyeglasses, consider adding anti-UV coatings to your lenses.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol can also help maintain eye health.
How Are Cataracts Diagnosed?
Diagnosing cataracts typically involves a thorough eye examination by an eye care professional. The evaluation may include:
- Visual Acuity Test: This test measures how well you can see at various distances and helps establish the extent of vision impairment.
- Dilated Eye Exam: Special drops are used to widen your pupils, allowing the doctor to examine the lens and retina in detail for any signs of cataracts.
- Slit-Lamp Examination: This test uses a microscope with a bright light to provide a magnified view of your eye, enabling the doctor to assess the presence and severity of cataracts.
Why Early Diagnosis Matters
If you notice any symptoms associated with cataracts, it’s important to consult your eye care provider promptly. Early diagnosis can lead to timely intervention, potentially preserving your vision and enhancing your overall quality of life.
At OptiCare Health, we prioritize your eye health and are committed to providing comprehensive eye care services tailored to your needs. If you have questions about your vision or would like to schedule an eye exam, don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
