Uveitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment You Should Know
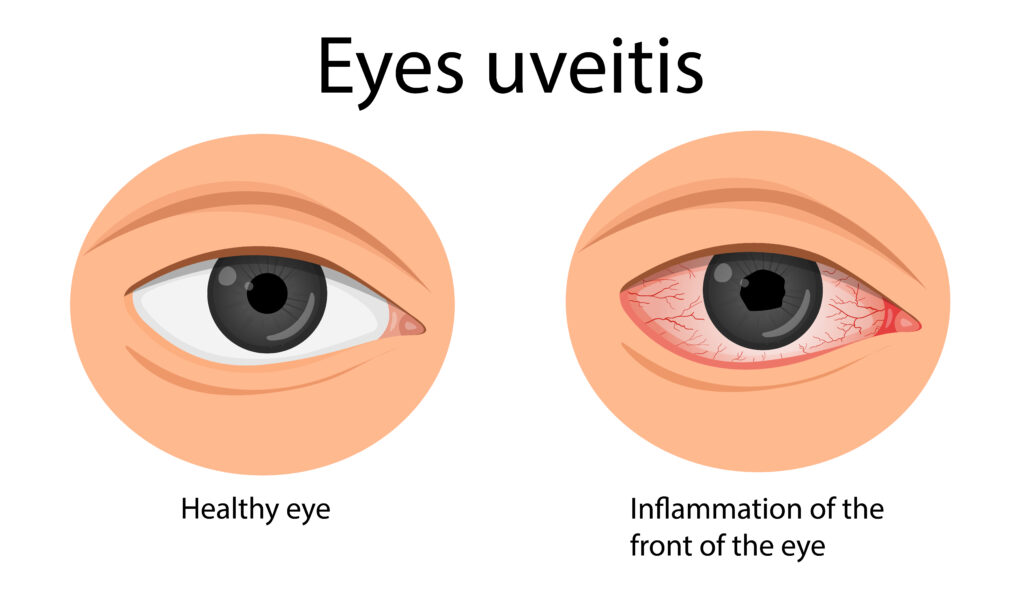
Uveitis is an inflammation inside the eye that affects the uvea, the middle layer of the eye containing the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. It can occur in one or both eyes, develop suddenly or gradually, and vary in severity. If left untreated, uveitis can lead to serious complications, including permanent vision loss. At OptiCare Health, we encourage early detection and personalized care to prevent long-term damage.
What Are the Symptoms and Signs of Uveitis?
The symptoms of uveitis can be subtle at first but often become noticeable as the inflammation progresses. Common signs include redness in one or both eyes, pain, light sensitivity (photophobia), blurred vision, and floaters—tiny dark spots that drift across your field of vision. Some people may also experience decreased vision or even sudden vision loss in severe cases.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to act quickly. Uveitis can cause complications like glaucoma, cataracts, and retinal damage if not treated in time. A comprehensive eye exam can confirm whether you have uveitis and determine the best course of action.
What Causes Uveitis and Who Is at Risk?
Uveitis can be caused by a variety of factors. In many cases, it’s linked to autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or ankylosing spondylitis. Infections like herpes, syphilis, or tuberculosis can also trigger inflammation inside the eye. Sometimes, uveitis results from eye injuries, surgeries, or even certain cancers, although these cases are less common.
Adults between the ages of 20 and 60 are most commonly affected, but uveitis can occur at any age. People with autoimmune conditions or chronic infections are at higher risk, as well as those with a history of eye trauma.
How Is Uveitis Treated and Why Early Diagnosis Matters
Treating uveitis promptly is critical to preventing vision loss. The most common treatment is corticosteroid eye drops, which help reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, oral steroids or injections may be required. If an infection is causing the inflammation, antiviral or antibiotic medications may be necessary. For chronic or autoimmune-related uveitis, immunosuppressive drugs can help control the condition.
At OptiCare Health, we provide comprehensive eye exams using advanced imaging technology to diagnose uveitis accurately. Our goal is to identify the underlying cause and create a personalized treatment plan. In addition, our Vision Simulator can help you understand how uveitis and other eye conditions can affect your vision if left untreated.
Protect Your Vision with Expert Care at OptiCare Health
If you’re experiencing any signs of uveitis, don’t wait for symptoms to worsen. Visit OptiCare Health in Brooklyn for a thorough eye exam and early treatment. Our experienced team is here to protect your vision and provide the care you need to maintain healthy eyes.
